In December Year 1 catalogs were printed for use in a special promotion in January Year
2. The catalogs were delivered by the printer on December 13. Year 1 with an invoice for
US $70,000 attached. Payment was made in January Year 2. The US $70.000 should be reported as a deferred cost at the December 31. Year I. balance sheet date because of the:
The basic formula for the Black-Schools Option Pricing Model essentially refs is The difference between the expected present value of the final stock price and the present value of the exercise price.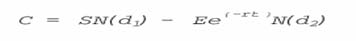
An entity wishes to price a call option written on a nondividend-paying stock using the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model. The current stock price is US $50, the exercise price is US $48. The risk-free interest rate is 5.0%, the option expires in 1 year, and the cumulative probabilities used to calculate the present values of the final stock price and the exercise price are 65 and 58 respectively. If the value of et-n) is .9512. the current value of the call option is:

Which of me following represents an inventory costing technique that can be manipulated by management to boost net income by selling units purchased at a low cost?
Which audit approach should be employed to test the accuracy of information housed in a database on an un-networked computer?
An entity sells a durable good to a customer on January 1, Year 1, and the customer is automatically given a 1-year warranty. The customer also buys an extended warranty package extending the coverage for an additional 2 years to the end of Year 3. At the time of the original sale, the company expects warranty costs to be incurred evenly over the life of the warranty contracts. The customer has only one warranty claim durln2 the 3-year period, and the claim occurs during Year 2. The company will recognize income from the sale of the extended warranty:
