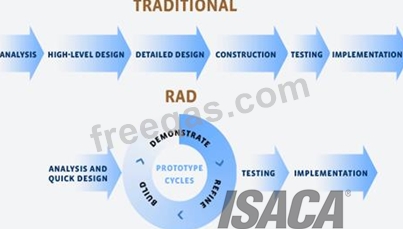
Section: Information System Operations, Maintenance and Support
Explanation:
The Work Recovery Time (WRT) determines the maximum tolerable amount of time that is needed to
verify the system and/or data integrity. This could be, for example, checking the databases and logs,
making sure the applications or services are running and are available. In most cases those tasks are
performed by application administrator, database administrator etc. When all systems affected by the
disaster are verified and/or recovered, the environment is ready to resume the production again.
For your exam you should know below information about RPO, RTO, WRT and MTD:
Stage 1: Business as usual
Business as usual

At this stage all systems are running production and working correctly.
Stage 2: Disaster occurs
Disaster Occurs

On a given point in time, disaster occurs and systems needs to be recovered. At this point the Recovery
Point Objective (RPO) determines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. For
example, the maximum tolerable data loss is 15 minutes.
Stage 3: Recovery
Recovery
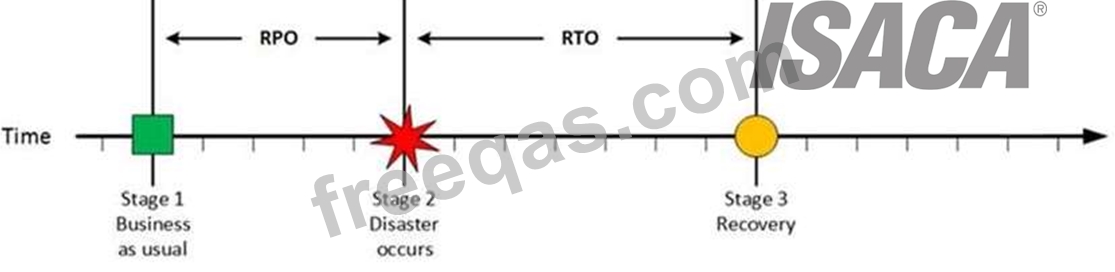
At this stage the system are recovered and back online but not ready for production yet. The Recovery
Time Objective (RTO) determines the maximum tolerable amount of time needed to bring all critical
systems back online. This covers, for example, restore data from back-up or fix of a failure. In most cases
this part is carried out by system administrator, network administrator, storage administrator etc.
Stage 4: Resume Production
Resume Production
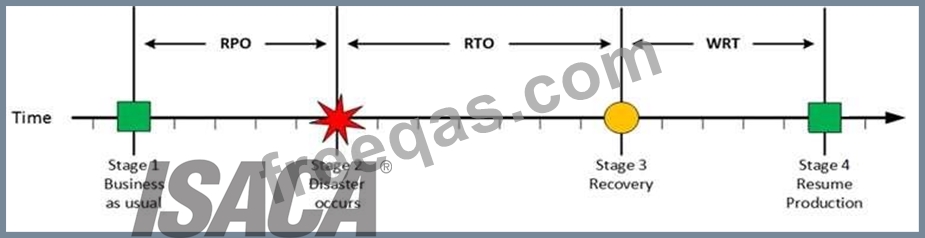
At this stage all systems are recovered, integrity of the system or data is verified and all critical systems can
resume normal operations. The Work Recovery Time (WRT) determines the maximum tolerable amount of
time that is needed to verify the system and/or data integrity. This could be, for example, checking the
databases and logs, making sure the applications or services are running and are available. In most cases
those tasks are performed by application administrator, database administrator etc. When all systems
affected by the disaster are verified and/or recovered, the environment is ready to resume the production
again.
MTD
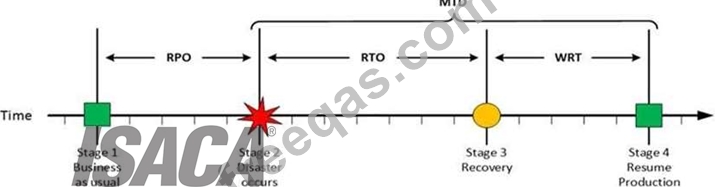
The sum of RTO and WRT is defined as the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) which defines the total
amount of time that a business process can be disrupted without causing any unacceptable consequences.
This value should be defined by the business management team or someone like CTO, CIO or IT
manager.
The following answers are incorrect:
RPO - Recovery Point Objective (RPO) determines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss
measured in time. For example, the maximum tolerable data loss is 15 minutes.
RTO - The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) determines the maximum tolerable amount of time needed to
bring all critical systems back online. This covers, for example, restore data from back-up or fix of a failure.
In most cases this part is carried out by system administrator, network administrator, storage administrator
etc.
MTD - The sum of RTO and WRT is defined as the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) which defines
the total amount of time that a business process can be disrupted without causing any unacceptable
consequences. This value should be defined by the business management team or someone like CTO,
CIO or IT manager.
References:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 284
http://defaultreasoning.com/2013/12/10/rpo-rto-wrt-mtdwth/