Explanation/Reference:
The word INCORRECTLY is the keyword used in the question. You need to find out a statement which is not valid about packet switching. As in the network switching, packet traverse different path, there will be always variable delay for each packet to reach to destination.
For your exam you should know below information about WAN message transmission technique:
Message Switching
Message switching is a network switching technique in which data is routed in its entirety from the source node to the destination node, one hope at a time. During message routing, every intermediate switch in the network stores the whole message. If the entire network's resources are engaged or the network becomes blocked, the message-switched network stores and delays the message until ample resources become available for effective transmission of the message.
Message Switching
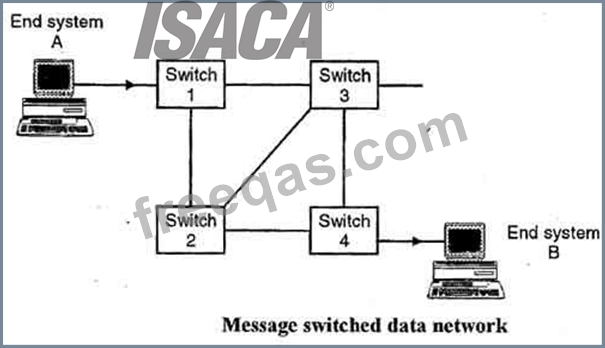
Image from: http://ecomputernotes.com/images/Message-Switched-data-Network.jpg Packet Switching
Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted individually and can even follow different routes to its destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at the destination, they are recompiled into the original message.
Packet Switching
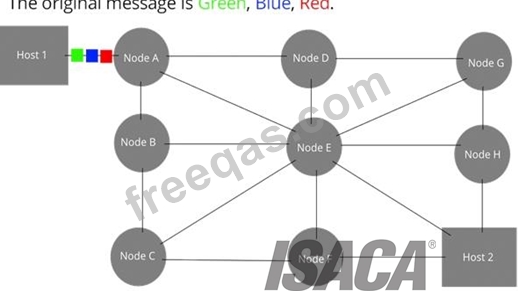
Image from: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f6/Packet_Switching.gif Circuit Switching
Circuit switching is a methodology of implementing a telecommunications network in which two network nodes establish a dedicated communications channel (circuit) through the network before the nodes may communicate.
The circuit guarantees the full bandwidth of the channel and remains connected for the duration of the session. The circuit functions as if the nodes were physically connected similar to an electrical circuit.
The defining example of a circuit-switched network is the early analog telephone network. When a call is made from one telephone to another, switches within the telephone exchanges create a continuous wire circuit between the two telephones, for as long as the call lasts.
In circuit switching, the bit delay is constant during a connection, as opposed to packet switching, where packet queues may cause varying and potentially indefinitely long packet transfer delays. No circuit can be degraded by competing users because it is protected from use by other callers until the circuit is released and a new connection is set up. Even if no actual communication is taking place, the channel remains reserved and protected from competing users.
Circuit Switching
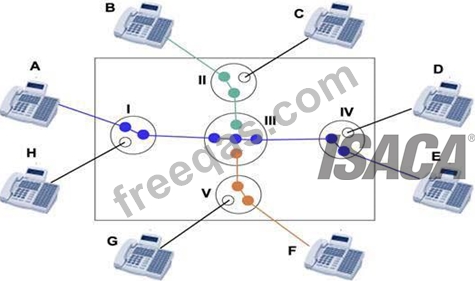
Image from: http://www.louiewong.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/Circuit_Switching.jpg See a table below comparing Circuit Switched versus Packet Switched networks:
Difference between Circuit and packet switching
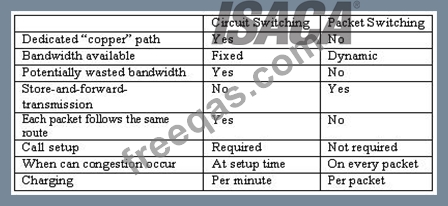
Image from:http://www.hardware-one.com/reviews/network-guide-2/images/packet-vs-circuit.gif Virtual circuit
In telecommunications and computer networks, a virtual circuit (VC), synonymous with virtual connection and virtual channel, is a connection oriented communication service that is delivered by means of packet mode communication.
After a connection or virtual circuit is established between two nodes or application processes, a bit stream or byte stream may be delivered between the nodes; a virtual circuit protocol allows higher level protocols to avoid dealing with the division of data into segments, packets, or frames.
Virtual circuit communication resembles circuit switching, since both are connection oriented, meaning that in both cases data is delivered in correct order, and signaling overhead is required during a connection establishment phase. However, circuit switching provides constant bit rate and latency, while these may vary in a virtual circuit service due to factors such as:
varying packet queue lengths in the network nodes,
varying bit rate generated by the application,
varying load from other users sharing the same network resources by means of statistical multiplexing, etc.
The following were incorrect answers:
The other options presented correctly describes about packet switching.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 265




