Section: Information System Operations, Maintenance and Support
Explanation/Reference:
For your exam you should know the information below related to LAN topologies:
LAN Topologies
Network topology is the physical arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer
network.
Essentially, it is the topological structure of a network, and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical
topology refers to the placement of the network's various components, including device location and cable
installation, while logical topology shows how data flows within a network, regardless of its physical design.
Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, and/or signal types may differ
between two networks, yet their topologies may be identical.
Bus
In local area networks where bus topology is used, each node is connected to a single cable. Each
computer or server is connected to the single bus cable. A signal from the source travels in both directions
to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the intended recipient. If the machine address does
not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores the data. Alternatively, if the data
matches the machine address, the data is accepted. Since the bus topology consists of only one wire, it is
rather inexpensive to implement when compared to other topologies. However, the low cost of
implementing the technology is offset by the high cost of managing the network. Additionally, since only one
cable is utilized, it can be the single point of failure. If the network cable is terminated on both ends and
when without termination data transfer stop and when cable breaks, the entire network will be down.
Bus topology
Graphic from:
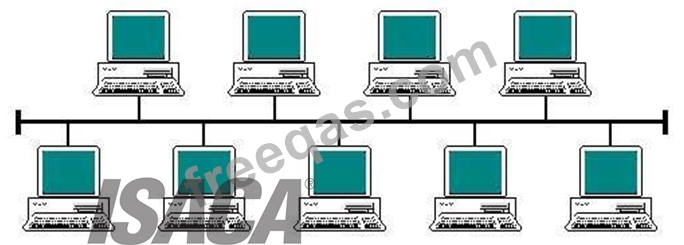
Linear bus
The type of network topology in which all of the nodes of the network are connected to a common
transmission medium which has exactly two endpoints (this is the 'bus', which is also commonly referred to
as the backbone, or trunk) - all data that is transmitted between nodes in the network is transmitted over
this common transmission medium and is able to be received by all nodes in the network simultaneously.
Distributed bus
The type of network topology in which all of the nodes of the network are connected to a common
transmission medium which has more than two endpoints that are created by adding branches to the main
section of the transmission medium - the physical distributed bus topology functions in exactly the same
fashion as the physical linear bus topology (i.e., all nodes share a common transmission medium).
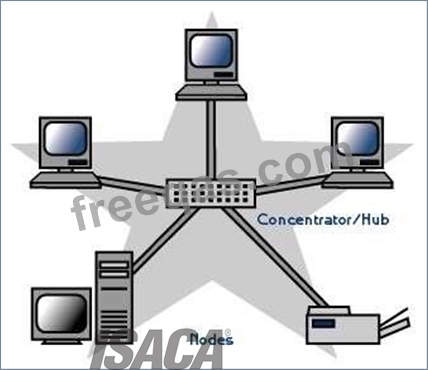
Star
In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central point with a point-
to-point connection. In Star topology every node (computer workstation or any other peripheral) is
connected to central node called hub or switch.
The switch is the server and the peripherals are the clients. The network does not necessarily have to
resemble a star to be classified as a star network, but all of the nodes on the network must be connected to
one central device.
All traffic that traverses the network passes through the central point. The central point acts as a signal
repeater.
The star topology is considered the easiest topology to design and implement. An advantage of the star
topology is the simplicity of adding additional nodes. The primary disadvantage of the star topology is that
the central point represents a single point of failure.
Star Topology
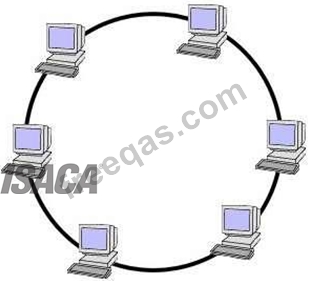
Ring
A network topology that is set up in a circular fashion in which data travels around the ring in one direction
and each device on the ring acts as a repeater to keep the signal strong as it travels. Each device
incorporates a receiver for the incoming signal and a transmitter to send the data on to the next device in
the ring.
The network is dependent on the ability of the signal to travel around the ring. When a device sends data, it
must travel through each device on the ring until it reaches its destination. Every node is a critical link. If
one node goes down the whole link would be affected.
Ring Topology
Mesh
The value of a fully meshed networks is proportional to the exponent of the number of subscribers,
assuming that communicating groups of any two endpoints, up to and including all the endpoints, is
approximated by Reed's Law.
A mesh network provides for high availability and redundancy. However, the cost of such network could be
very expensive if dozens of devices are in the mesh.
Mesh Topology
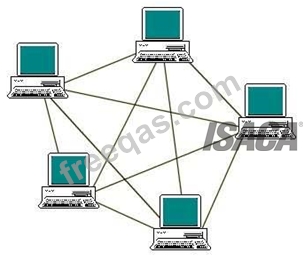
Fully connected mesh topology
A fully connected network is a communication network in which each of the nodes is connected to each
other. In graph theory it known as a complete graph. A fully connected network doesn't need to use
switching nor broadcasting. However, its major disadvantage is that the number of connections grows
quadratic ally with the number of nodes, so it is extremely impractical for large networks. A two-node
network is technically a fully connected network.
Partially connected mesh topology
The type of network topology in which some of the nodes of the network are connected to more than one
other node in the network with a point-to-point link - this makes it possible to take advantage of some of
the redundancy that is provided by a physical fully connected mesh topology without the expense and
complexity required for a connection between every node in the network.
The following answers are incorrect:
The other options presented are not valid.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014, Page number 262





