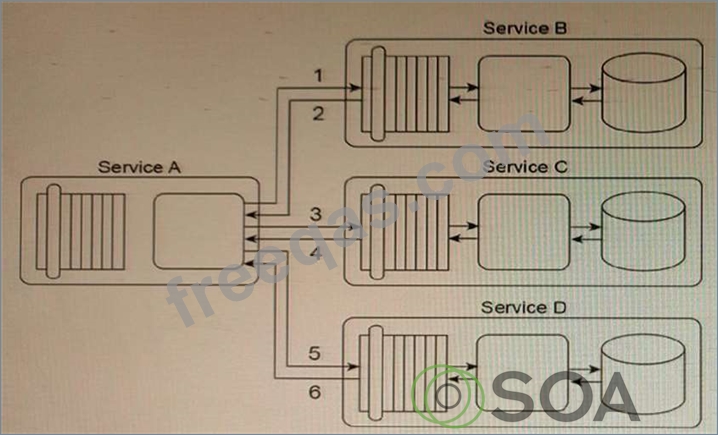
Service A is a task service that is required to carry out a series of updates to a set of databases in order to complete a task. To perform the database updates. Service A must interact with three other services that each provides standardized data access capabilities.
Service A sends its first update request message to Service B (1), which then responds with a message containing either a success or failure code (2). Service A then sends its second update request message to Service C (3), which also responds with a message containing either a success or failure code (4). Finally, Service A sends a request message to Service D (5), which responds with its own message containing either a success or failure code (6).
Services B, C and D are agnostic services that are reused and shared by multiple service consumers. This has caused unacceptable performance degradation for the service consumers of Service A as it is taking too long to complete its overall task. You've been asked to enhance the service composition architecture so that Service A provides consistent and predictable runtime performance. You are furthermore notified that a new type of data will be introduced to all three databases. It is important that this data is exchanged in a standardized manner so that the data model used for the data in inter-service messages is the same.
What steps can be taken to fulfill these requirements?
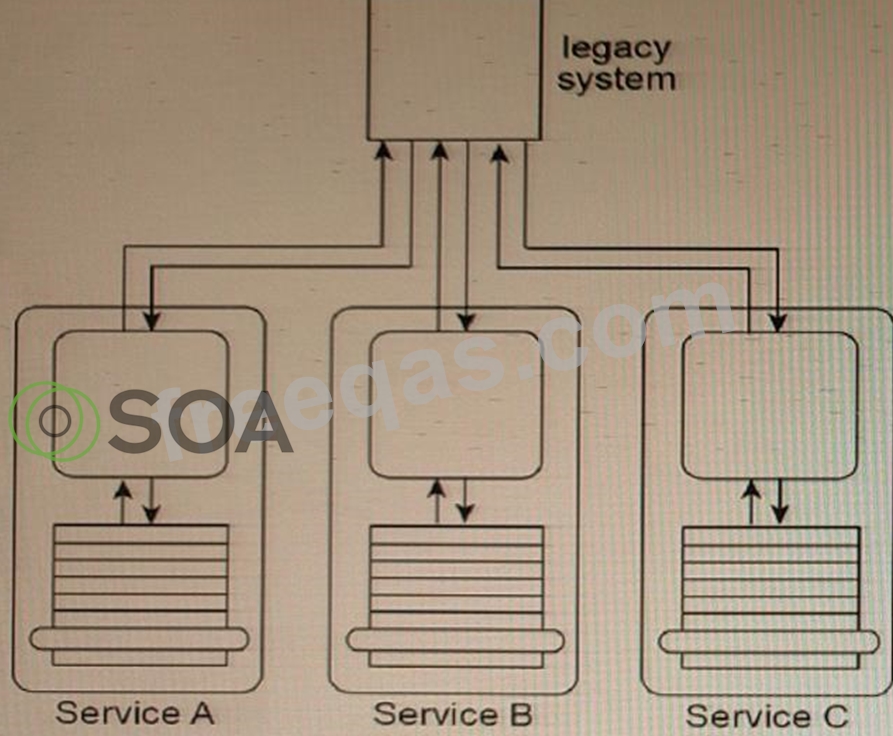
Service A, Service B, and Service Care entity services, each designed to access the same shared legacy system.
Service A manages order entities, Service B manages invoice entities, and Service C manages customer entities. Service A, Service B, and Service C are REST services and are frequently reused by different service compositions. The legacy system uses a proprietary file format that Services A, B, and C need to convert to and from.
You are told that compositions involving Service A, Service B, and Service C are unnecessarily complicated due to the fact that order, invoice, and customer entitles are all related to each other. For example, an order has a customer, an invoice has an order, and so on. This results In calls to multiple services to reconstruct a complete order document. You are asked to architect a solution that will simplify the composition logic by minimizing the number of services required to support simple businessfunctions like order management or bill payment. Additionally, you are asked to reduce the amount of redundant data transformation logic that is found in Services A, B, and C.
How will you accomplish these goals?
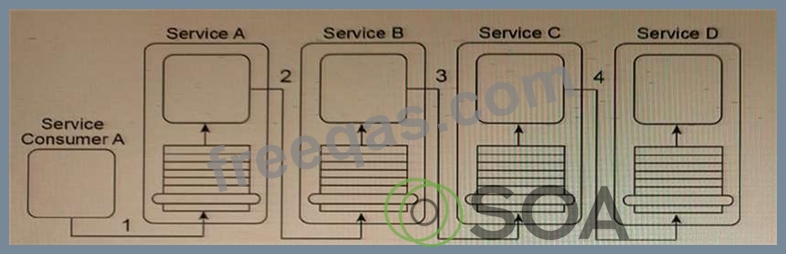
Service Consumer A sends a message to Service A (1), which then forwards the message to Service B (2).
Service B forwards the message to Service C (3), which finally forwards the message to Service D (4).
However, Services A, B and C each contain logic that reads the contents of the message to determine what intermediate processing to perform and which service to forward the message to. As a result, what is shown in the diagram is only one of several possible runtime scenarios.
Currently, this service composition architecture is performing adequately, despite the number of services that can be involved in the transmission of one message. However, you are told that new logic is being added to Service A that will require it to compose one other service to retrieve new data at runtime that Service A will need access to in order to determine where to forward the message to. The involvement of the additional service will make the service composition too large and slow.
What steps can be taken to improve the service composition architecture while still accommodating the new requirements and avoiding an increase in the amount of service composition members?
Refer to Exhibit.
Service Consumer A sends a message to Service A (1), which then forwards the message to Service B (2). Service B forwards the message to Service C (3), which finally forwards the message to Service D (4). However, Services A, B and C each contain logic that reads the contents of the message to determine what intermediate processing to perform and which service to forward the message to. As a result, what is shown in the diagram is only one of several possible runtime scenarios.
Currently, this service composition architecture is performing adequately, despite the number of services that can be involved in the transmission of one message. However, you are told that new logic is being added to Service A that will require it to compose one other service to retrieve new data at runtime that Service A will need access to in order to determine where to forward the message to. The involvement of the additional service will make the service composition too large and slow.
What steps can be taken to improve the service composition architecture while still accommodating the new requirements and avoiding an increase in the amount of service composition members?
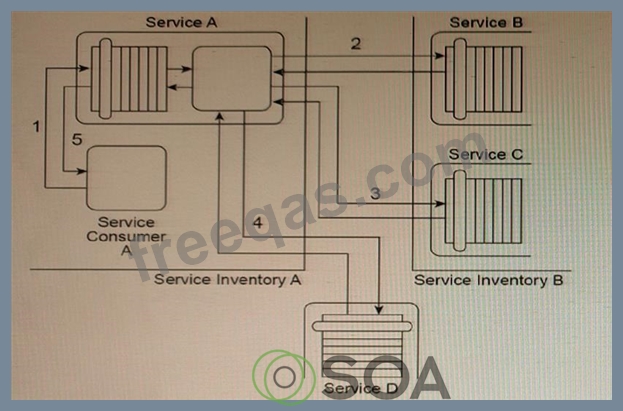
Service Consumer A and Service A reside in Service Inventory A. Service B and Service C reside in Service Inventory B. Service D is a public service that can be openly accessed via the World Wide Web. The service is also available for purchase so that it can be deployed independently within IT enterprises. Due to the rigorous application of the Service Abstraction principle within Service Inventory B, the only information that is made available about Service B and Service C are the published service contracts. For Service D, the service contract plus a service level agreement (SLA) are made available. The SLA indicates that Service D has a planned outage every night from 11:00pm to midnight.
You are an architect with a project team that is building services for Service Inventory A. You are told that the owners of Service Inventory A and Service Inventory B are not generally cooperative or communicative.
Cross-inventory service composition is tolerated, but not directly supported. As a result, no SLAs for Service B and Service C are available and you have no knowledge about how available these services are. Based on the service contracts you can determine that the services in Service Inventory B use different data models and a different transport protocol than the services in Service Inventory A. Furthermore, recent testing results have shown that the performance of Service D is highly unpredictable due to the heavy amount of concurrent access it receives from service consumers from other organizations. You are also told that there is a concern over how long Service Consumer A will need to remain stateful while waiting for a response from Service A.
What steps can be taken to solve these problems?
