Refer to the exhibit.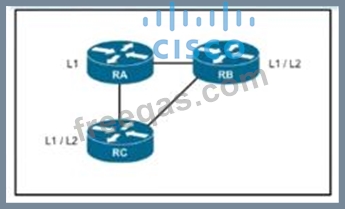
Routers RA and RB are IS-IS peers configured for NSF but router RC is an IS-IS peer without NSF capability If RA undergoes processor switchover what is the effect on the network environment?

Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer implemented this segment routing configuration. Which statement about the output is true?
When deploying a nationwide network of routers, what is the benefit of using BGP confederations?
What is one of the purposes of a default Multicast Distribution Tree?
After an engineer configures BGP in R1, it starts receiving this message
*Jun 29 13:30:50.122: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 192.168.10.1 Down User reset Jun 29 13:30:52.341: %BGP-3-NOTIFICATION: sent to neighbor 192.168.10.1 2/6 (unacceptable hold time) 0 bytes Which action makes the peering come back up again?
